|
Ningbo Joy Industrial & Trading Co.,Ltd.
|
Special Magnet Shield Neodymium Magnetic Shield
| Price: | 0.1~10.0 USD |
| Payment Terms: | T/T,L/C |
| Place of Origin: | Zhejiang, China (Mainland) |
|
|
|
| Add to My Favorites | |
| HiSupplier Escrow |
Product Detail
Shields are punched & bent or punched and deep drawn for various applications like electricity meters, electronic control protections in many devices
Introduction of Shields
We are surrounded by magnetic fields (both AC and DC) from the earth's magnetic field to man-made sources such as magnets,motors and transformers. To avoid effect of this field on sensitive equipments, magnetic shielding is required. e.g. cathode ray tubes, photomultiplier tubes, audio transformers, scanning electron microscopes, position sensors.
The shield is made of soft ferromagnetic material with a high Permeability (μ). 36%, 48% &80% NiFe are most commonly used soft magnetic alloys. In order to have a low Hysteresis, the shield is annealed after shaping. Any stress after annealing will deteriorate the performance and hence should be avoided.


How does a magnetic shield work?
There is no known material that can block magnetic fields without itself being attracted to the magnetic force. A magnetic shield acts as a kind of sponge redirecting the magnetic field around the shield instead of passing through the sensitive instrument which is being shielded. A good magnetic shielding material must have high permeability which means that the magnetic field lines are strongly attracted to the shielding material. If the magnetic field is too high for the material chosen it will saturate and become ineffective. In this case, a multi layer shield with a combination of the above alloys can be used.
Shielding Factor:
The Shielding Factor is defined as the ratio between the external and the internal field when the shield is placed in an area with a homogenous magnetic field.
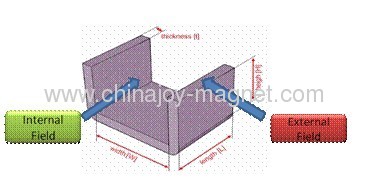

The Shielding Factor is defined as the ratio between the external and the internal field when the shield is Shielding Factor = External Field / Internal Field.
Saturation:
The magnetic saturation of the shield is given by the magnetic properties of the shield material.
Ferromagnetic material saturates between 0.5 and 2 Tesla. Once the shield is saturated, its apparent Permeability will decline to the value 1, meaning that the shield acts like air. A saturated shield does not guide nor attract magnetic flux lines. Therefore, the shield design has to be chosen such that the field generated by the current and the field generated by external sources do not saturate the shield material.
Magnetic Shielding Definitions
Property | Unit | Formula | Definition | |
1 | Attenuation (g) | -- | g= Ho/ Hin | Ho : Field intensity outside in Oersteds (Oe), Hi : Field intensity inside in Oersteds (Oe) |
2 | Shielding Efficiency (SE) | dB | 20log o. g | |
3 | % shielding | (1-1/g) x 100 | ||
4 | Attenuation in Uniform DC field ( g DC) | (µ/4) x (1-a²/b²) | µ - Permeability of Material in Gauss | |
a - Inner radius of shield | ||||
b - Outer radius of shield | ||||
t - thickness of shield | ||||
(µ/4) x (T/b) (2-T/b)≈µT/2b | Shielding effectiveness depends only on the permeability of the material and the ratio of wall thickness to outer radius. This holds true for cylinders with a length to diameter ratio of 4 or more | |||
5 | Attenuation in AC field g (AC) | Designing for a DC field provides a maximized shield in AC fields of equal density ( AC Peak) | ||
Field Strength (H) | Oersteds(Oe) | lines/cm² in Air | ||
Flux Density(B) | Gauss (G) | lines/cm² in Air | ||
Permeability (µ) | µ=B/H | measure of material's capability to conduct magnetic lines of force or flux | ||
Magnetic saturation level | The flux level at which the material can no longer conduct any additional lines of force. | |||
Reluctance ( R ) | R = l/µA | The measure of material's resistance to the passage to magnetic flux. l = flux path length (cm), A = cross sectional area (cm²) |
What we can Offer:
Shields which are punched & bent or punched and deep drawn for various applications like electricity meters, electronic control protections in automobiles, avionics, medical devices, audio devices.



Didn't find what you're looking for?
Post Buying Lead or contact
HiSupplier Customer Service Center
for help!








